If you aim for nothing, you'll achieve it every time.
Many organisations struggle (or are not even trying) to build their internal organisational change management capability, often relying on external consultants to save troubled projects or simply not seeing the expected return on investment. To help address this struggle, Sortd has developed the Sortd Organisational Change Maturity Model, a detailed model based on 4 key influencers assessed using practical real-life examples and supported by the Sortd Organisational Change Management Platform. The Sortd Organisational Change Maturity Model is based on years of research from global leaders in change including McKinsey & Company, Change Management Institute, and Prosci.
By setting goals and tracking progress towards them, organisations can truly see the value created when change is successfully executed.
Influencers of Change
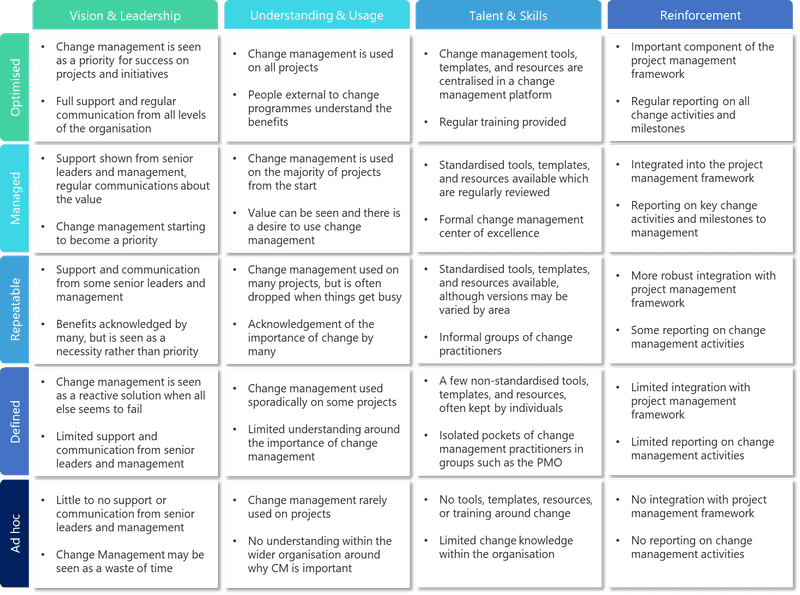
We start with the 4 influencers of change, these are the building blocks of creating a culture of change within an organisation. They have been designed to support changing environments within organisations by:
- Providing role models for change - when people see their leaders and colleagues behaving differently, they will often mimic this behaviour - whether conciously or unconciously (Vision & Leadership)
- Enabling a culture of understanding the why - congruence between beliefs and actions inspires people to behave in a way which supports change (Understanding)
- Giving people the skills, knowledge, and training necessary to behave in new ways (Talent & Skills)
- Helping people learn through consistency and repetition, as well as ensuring structures, processes, and systems support the changes being asked. All too often organisations have misaligned associations and concequences resulting in reinforcing the wrong behaviour (Reinforcement)
Vision & Leadership
This area focuses on ensuring the necessary vision & leadership are present within the organisation. Are the right sponsors in place? Is communication delivered consistently and in the right format? Is organisational change management seen as a priority or a necessity?
Understanding
This area focuses on assessing how organisational change management is understood within the organisation. Do people have an understanding of why they are carrying out activities? Have they seen success using change management previously? Is there a centralised group of change practitioners?
Talent & Skills
This area focuses on ensuring the people within the organisation are supported with the right skills and training to excel at embeddeding and maintaining change. Are standardised tools, templates, and resources available? Does the organisation have training resources around change?
Reinforcement
As the late Anthony Bourdain once said:
We learn as professionals by repetition, by getting it wrong, getting yelled at and doing it again.
Maybe we can skip the getting yelled at part, but the principle remains the same. As its name suggests the key focus of this area is ensuring that change management efforts are done in a consistent coordinated manner, enabling organisations to change, learn, and repeat. Is organisational change management present throughout the organisation or isolated in certain pockets? Is organisational change management integrated with the organisations project management framework? Is organisational change management reported on and actively improved?
The 5 Levels of Maturity
Ad hoc
When an organisation is at the lowest level of maturity, change management can be seen as a distraction from delivering technical solutions/projects and often simply a waste of time. If change management is used, it is often as a last resort when everything else seems to fail. There is little to no support from senior leadership, and very little desire from individuals to make an effort.
Organisations at this level may experience a high rate of change failure, staff experiencing change fatigue, and an overall lack of foresight into the direction of the organisation.
Defined
When an organisation has reached the Defined level of change maturity, change management may become important to some, but remains unimportant to most. When change management is used, it is often used selectively or sporadically, often in reaction to resistance to change. There may be a few tools, templates, and resources available for use (behind the coffee machine perhaps?) and if someone knows someone who knows someone, they may just be able to get access to these resources. Change practitioners are often in isolated pockets and use their own knowledge rather than relying on an organisaiton framework.
Organisations at this level have greater success at embedding change than at the Ad Hoc level, however may find that success varies greatly from project to project depending on a variety of factors.
Repeatable
When an organisation reaches the Repeatable level of change maturity, change management may be acknowledge by many, but is still often seen as the first thing to drop when times are tough. Organisations at this level have a structured approach which adds value when it is used and change management activities is still not often included as part of the project management framework. There will likely be a set of tools, templates, and resources available for use, often with multiple versions scattered around the organisation. Change practitioners start to work together, sometimes creating an unofficial center of excellence to share knowledge, and this is supported by at least some senior leaders and managers.
Managed
Organisations at the Managed level of change maturity can show a lot of value attributed to the use of change management. It is generally acknowledged throughout the entire organisation as an important success factor and has a unified approach. Change management is used on most projects, and is integrated into the project management framework, including key change milestones. Organisations at this level will have a set of tools, templates, and resources that are fit for purpose and regularly reviewed. Change management is used and considered by most project teams and functional business areas, senior leadership, managers, and supervisors. There is often a formalised center of excellence to share knowledge and resources.
Optimised
When an organisation reaches the pinnacle of maturity, Optimised, change management is no longer an activity to be undertaken, it is how things are done. It becomes a core competency for the entire organisation and is used on all projects and initiatives. The project management framework and change management framework become one, and project and change teams work together as one to drive results. Organisations at this level will often use a change management platform to manage change activies, have regular reviews of the quality of tools, templates, and resources, and have a continuous improvement mindset. Change management is used by all project teams, functional business units, and leadership. There will be a formalised centre of excellence.
The Framework
The 4 areas of focus combined with the 5 levels of maturity combine to form the Sortd Organisational Change Maturity Model.
Sortd Platform
Traditional organisational change management tools are disjointed, static, and can end up creating more pain than value. That's why we created the Sortd Organisational Change Management Platform. The platform incorporates a wide variety of traditional change management tools, as well as some new ones built just for you.
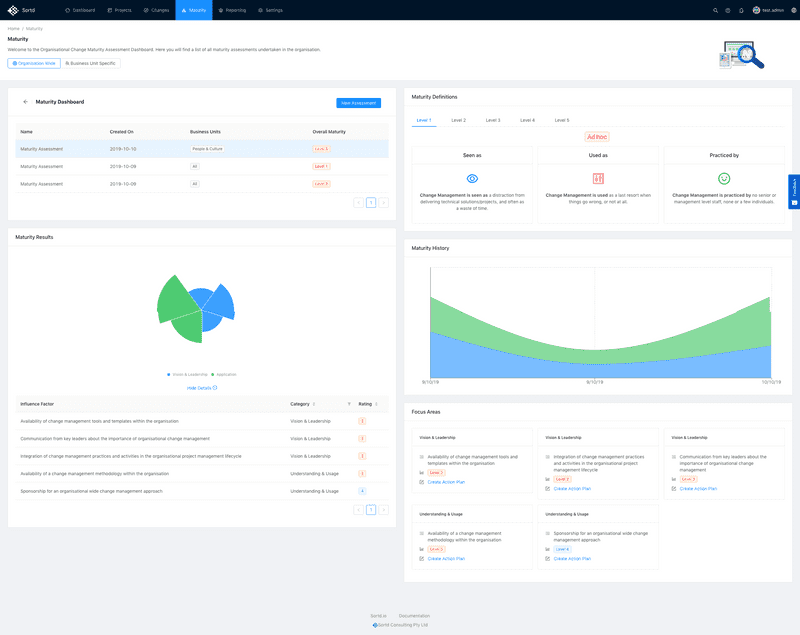
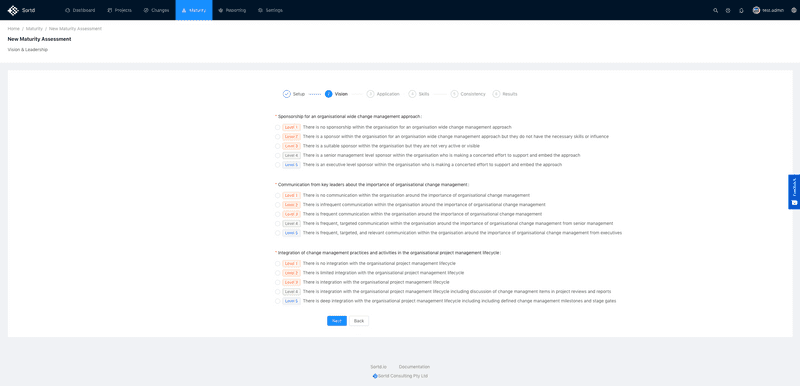
One such tool is the Change Maturity Assessment tool, which enables organisations to consistently track and rate their change maturity. The tool follows an easy to follow questionaire style rating system based on real world practical examples and enables detailed reporting and action plans to be created.
If you're interested in getting your change #Sortd, get in touch today.